Pan of M83 (NIRCam image)
Description
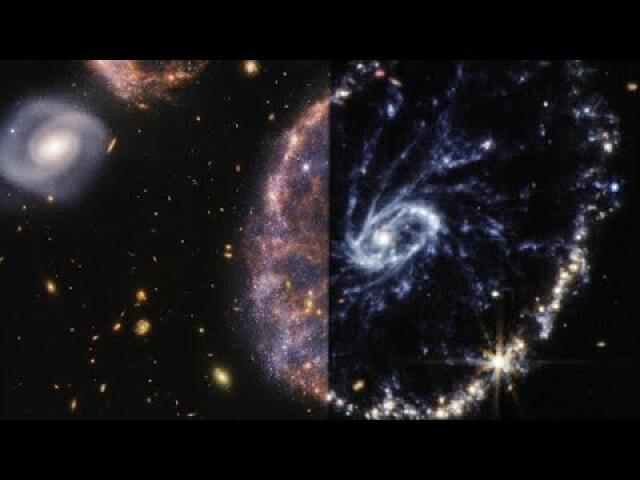
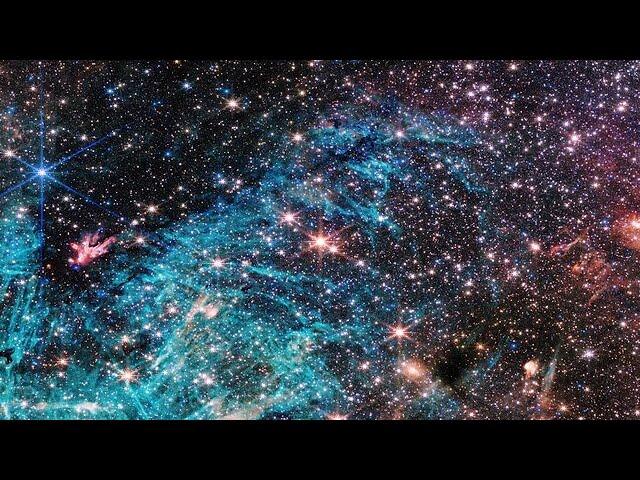
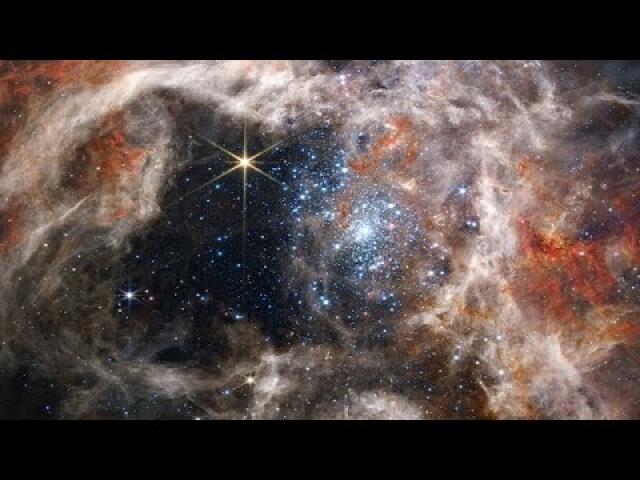
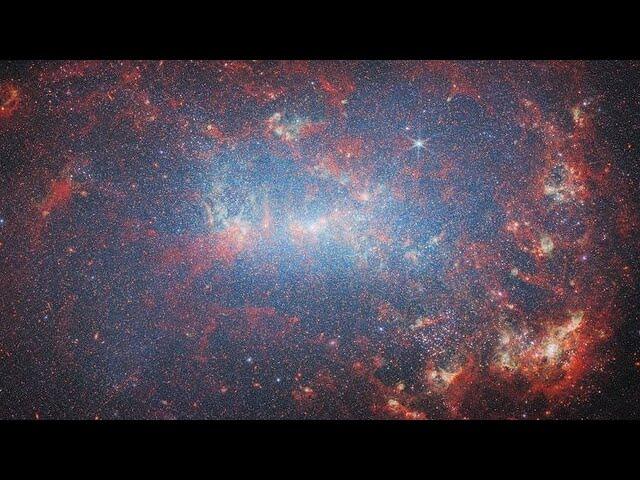
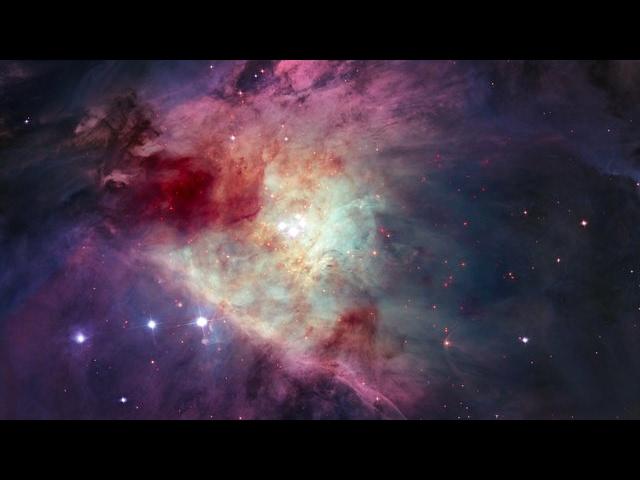
This image was captured by Webb’s NIRCam, or Near-InfraRed Camera. NIRCam makes observations in the near-infrared, which spans wavelengths of light that are just longer than optical wavelengths. Like MIRI, it is equipped with a range of filters that cover its wavelength range of 0.6 to 5 micrometres, including 29 filters specifically intended for imaging. Data collected through eight of those filters were used to complete this impressive image, which picks out light emitted from the wealth of stars that might be obscured by dust at other wavelengths. Even though stars do not emit the majority of their light in the infrared, optical light is much more vulnerable to being scattered by dust than infrared light is, and so infrared instruments like Webb can provide the best opportunities to study stars in regions (like galaxies) that might also contain large amounts of dust.
In this image, the bright red-pink spots correspond to regions rich in ionised hydrogen, which is due to the presence of newly formed stars. The diffuse gradient of blue light around the central region shows the distribution of older stars. The compact light blue regions within the red, ionised gas, mostly concentrated in the spiral arms, show the distribution of young star clusters.
More information and download options: http://esawebb.org/videos/potm2310b/
Credit:
ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, A. Adamo (Stockholm University) and the FEAST JWST team, N. Bartmann (ESA/Webb)
Music: Stellardrone - The Edge of Forever