Time Travel, Teleportation & Science
Time travel is the concept of moving between different points in time in a manner analogous to moving between different points in space, generally using a theoretical invention, namely a time machine. It has a commonly recognized place in philosophy and fiction, but has a very limited application in real world physics, such as in quantum mechanics or wormholes.
Although the 1895 novel The Time Machine by H. G. Wells was instrumental in moving the concept of time travel to the forefront of the public imagination, The Clock That Went Backward by Edward Page Mitchell was published in 1881 and involves a clock that allowed three men to travel backwards in time.[1][2] Non-technological forms of time travel had appeared in a number of earlier stories such as Charles Dickens' A Christmas Carol. Historically, the concept dates back to the early mythologies of Hinduism (such as the Mahabharata), Buddhism, and Islam through ancient folk tales. More recently, with advancing technology and a greater scientific understanding of the universe, the plausibility of time travel has been explored in greater detail by science fiction writers, philosophers, and physicists.
Teleportation, or Teletransportation, is the theoretical transfer of matter or energy from one point to another without traversing the physical space between them. It has a commonly recognized place in science fiction literature, film, and television, but as yet has a very limited application in real world physics, such as quantum teleportation or the study of wormholes.
Science (from Latin scientia, meaning "knowledge") is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. In an older and closely related meaning, "science" also refers to a body of knowledge itself, of the type that can be rationally explained and reliably applied. A practitioner of science is known as a scientist.
In modern usage, "science" most often refers to a way of pursuing knowledge, not only the knowledge itself. It is also often restricted to those branches of study that seek to explain the phenomena of the material universe.
Source : Wikipedia
-
01:00

Methane mitigation
Added 131 Views / 0 LikesResearchers have developed a powdered catalyst that can promote the otherwise natural conversion of methane to carbon dioxide in a matter of seconds. With this technique methane can be removed from the air completely.
-
01:01

The Oldest Camera Photograph
Added 122 Views / 0 Likes"View from the Window at Le Gras": the earliest-known (and perhaps first!) photograph taken with a camera ????#photography #history #Nicéphore #Niépce #France #LaGras #pewter #bitumen #austin #austintx #utaustin #historyofphotography #reality #media #vsau
-
04:36

Moooving the needle on methane
Added 145 Views / 0 LikesWith a newly developed catalyst, researchers are working to set up systems to reduce methane in the air at dairy farms and other sites. "Methane emission removal is the fastest way that we can ensure immediate results for reduced global warming." Graduate
-
1:12:06

Why a Forefather of AI Fears the Future
Added 124 Views / 0 LikesA renowned AI pioneer explores humanity's possible futures in a world populated with ever more sophisticated mechanical minds.This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.Participants:Yoshua BengioModerator:Bria
-
01:01

A Marble-Powered Computer
Added 117 Views / 0 Likeshttps://www.tiktok.com/@corndogwillyhttps://www.instagram.com/electricpantshttps://www.facebook.com/VsauceGaming/
-
25:16

Curiosity Unbounded, Episode 8: Hard facts on soft skills
Added 131 Views / 0 LikesNamrata Kala is an associate professor in applied economics at the MIT Sloan School of Management. She studies the value of employee training and incentives, how communities adapt to environmental change and regulation, and the returns on environmental te
-
1:26:58

AI and Quantum Computing: Glimpsing the Near Future
Added 149 Views / 0 LikesCatch a glimpse of the near future as AI and Quantum Computing transform how we live. Eric Schmidt, decade-long CEO of Google, joins Brian Greene to explore the horizons of innovation, where digital and quantum frontiers collide to spark a new era of disc
-
00:44
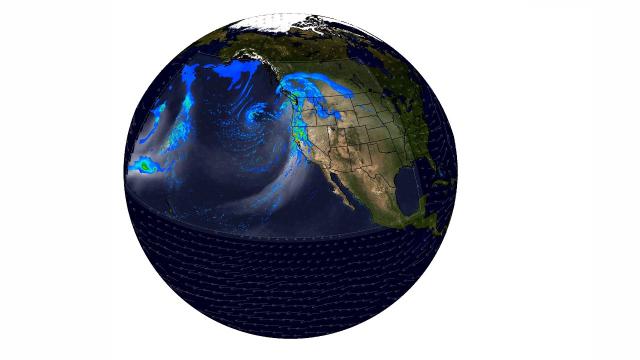
Algorithm helps forecast frequency of extreme weather
Added 127 Views / 0 LikesBy combining machine learning with dynamical systems theory, a team at MIT have now developed a method to "correct" the predictions from coarse climate models. The team’s approach “nudges” a climate model’s simulations into more realistic patterns over la
-
00:13

New system monitors and controls spraying
Added 128 Views / 0 LikesIn field tests, MIT spinoff AgZen demonstrated that its feedback-optimized spraying system could halve the pesticide needs of farms and improve crop yields. (Learn more: https://news.mit.edu/2024/reducing-pesticide-use-while-increasing-effectiveness-agzen
-
30:20

Beyond Einstein: Part One - Gravitational Rainbows
Added 139 Views / 0 LikesBEYOND EINSTEIN is a 3-part series exploring the wondrous implications of gravity pushed to the extreme, tackling dark energy, black holes and white holes. Renowned researchers join Brian Greene to discuss a range of insights–from confirmed to highly spec
-
35:33

Beyond Einstein: Part Two - Gravitational Echoes
Added 136 Views / 0 LikesPart 2 | Gravitational Echoes: Just as sound waves can echo off a distant rockface, light waves can echo off of black holes. Renowned researchers Erin Kara and Shep Doeleman join Brian Greene to explore the exotic physics that rules all that happens near









